| Protease / enzyme-cleavable |
Cathepsin-type: Val–Cit, Val–Ala, Phe–Lys (and tuned analogs)
MMP motifs: PLGLAG, GPLGVR (and variants)
Caspase motifs: DEVD, IETD (and variants)
Legumain: AAN-type sequences
Also used (context-specific): PSA / uPA / elastase / thrombin motifs
|
Highest-use class for targeted release. Often paired with a
self-immolative spacer to release an
amine-bearing payload cleanly (classic ADC pattern: protease trigger → PABC → payload).
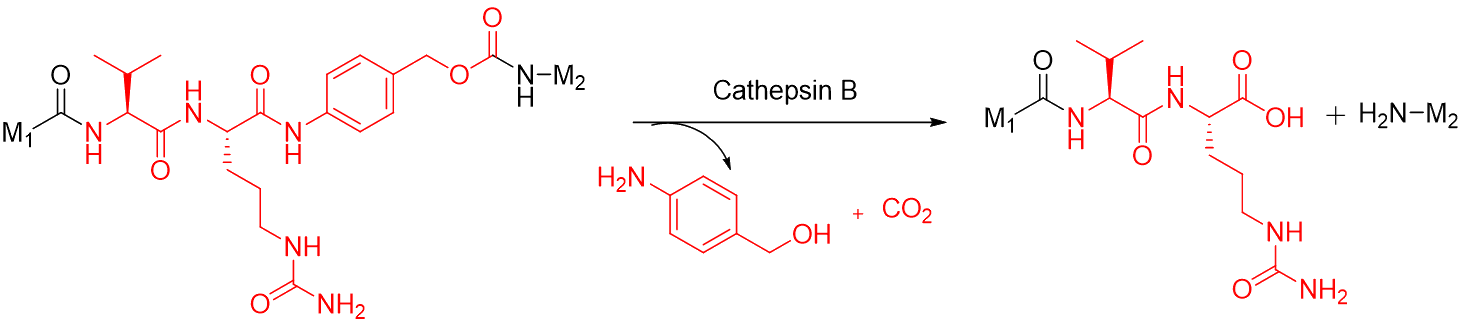 Representative protease-cleavable (Val–Cit–PABC) mechanism showing
cathepsin-B activation and self-immolative payload release.
Representative protease-cleavable (Val–Cit–PABC) mechanism showing
cathepsin-B activation and self-immolative payload release.
|
| Glycosidase / lysosomal enzyme-cleavable |
β-Glucuronide linkers (plus related glycoside triggers in some designs) |
Enzyme trigger + self-immolation is common; useful when you want strong lysosomal specificity. |
| pH-sensitive / acid-labile |
Hydrazone; Acetal/Ketal; cis-Aconityl; Orthoester (specialized) |
Designed for endosome/lysosome acidity. Best when you want environment-only activation without enzyme dependence.
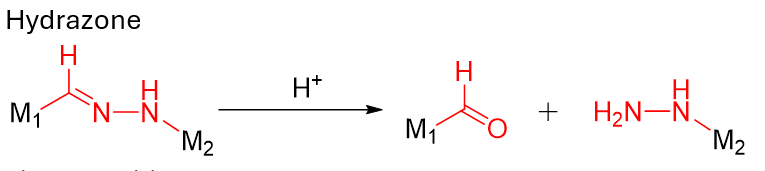 Hydrozone linker
Hydrozone linker
|
| Redox-responsive |
Disulfide; sterically hindered disulfides (tuned); Diselenide (specialized) |
Popular for intracellular release. Sterics/placement strongly affect serum stability vs cytosolic cleavage.
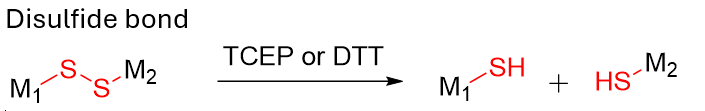 Redox-responsive, disulfide linkers
Redox-responsive, disulfide linkers
|
| ROS / oxidative-stress responsive |
Thioketal (ROS-cleavable); boronate/boronic ester triggers (context-specific); oxidation-fragmentation motifs (design-dependent) |
Useful for inflammatory/tumor microenvironments with elevated ROS; common in responsive delivery systems. |
| Hypoxia-responsive |
Azo (bioreductive); nitroaromatic triggers (bioreductive activation; design-dependent) |
More specialized; best when targeting hypoxic tumor regions. Validate enzyme expression in your model. |
| Photo-cleavable |
o-Nitrobenzyl (ONB) family; coumarin-based cages; nitroveratryl variants |
Spatial/temporal control (“uncaging”). Useful for capture/release and controlled activation.
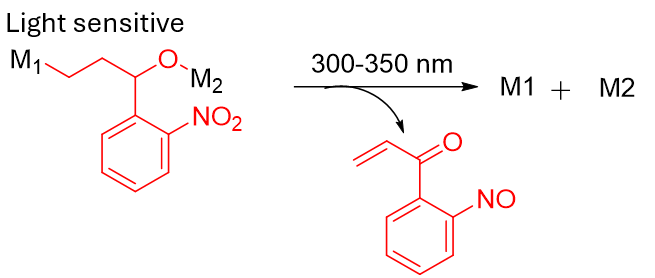 photo-cleavable, light sensitive linkers
photo-cleavable, light sensitive linkers
|
| Click-to-release |
Tetrazine-triggered release from TCO-derived linkers (“click-to-release” family); other triggerable IEDDA designs |
Two-step control: stable until an external trigger reagent is added. Strong for conditional activation workflows. |
| Self-immolative spacers |
PABC / PAB-type para-aminobenzyl spacers; carbonate/carbamate self-immolation variants |
Not a trigger by itself—this is the release module that converts a trigger event into clean payload liberation (especially for amines). |
| Chemically cleavable (exogenous trigger) |
Periodate-cleavable motifs (design-dependent); metal-assisted cleavage (specialized); oxidation-cleavable “lab handles” (specialized) |
Used when you want on-demand cleavage in vitro (purification workflows, capture/release assays). Validate compatibility with peptide and payload. |
| Traceless release designs |
Architectures that regenerate the native functional group (amine/thiol/alcohol) with minimal “scar” |
Often achieved via self-immolation or rearrangement; important when activity requires the native terminus/side chain. |